Truths About Radon
US EPA
Is radon really bad for you?
Breathing radon over time increases your risk of lung cancer. Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States. Nationally, the EPA estimates that about 21,000 people die each year from radon-related lung cancer. Only smoking causes more lung cancer deaths.
The incident dramatized the reality that radon levels in particular dwellings can occasionally be orders of size higher than common. Radon quickly came to be a standard property owner concern, though http://www.Radon1.com typical residential exposures are a couple of orders of size lower (100 Bq/m3, or 2.5 pCi/L), making individual testing essential to assessment of radon threat in any type of specific dwelling. Radon doesn't cause scratchy eyes or sprinkling noses, yet it does harm your lungs gradually. Long-lasting direct exposure throughout years, even if radon levels rise and drop in time, dramatically raises your chances of developing lung cancer cells. Since you're investing hrs each time in your house breathing in the air, you're mosting likely to absorb lots of radon as you prepare, bathe, and also sleep if it's present in the residence's air supply.
Persistent direct exposure to radon gas enhances the risk of developing lung cancer cells. In the USA, an approximated 21,000 individuals pass away from radon-related lung cancer yearly (compared to 160,000 lung cancer fatalities from smoking cigarettes), according to the EPA. Radon is the second leading reason for lung cancer, as well as it's the leading source of lung cancer cells in nonsmokers, according to the company.
Is radon mitigation really necessary?
When radon gas enters the body, it exposes the lungs to small amounts of radiation. In small quantities, experts say this is harmless. However, in persistent exposures or larger quantities, radon can damage the cells of the lining of the lungs, increasing a person's chance of developing lung cancer.
The United States EPA has actually put it plainly, stating, "Any radon exposure has some threat of creating lung cancer cells. Radon gas is a naturally-occurring by-product of the radioactive decay of Uranium in the dirt. Relying on your geographic place, the radon degrees of the air you take a breath outside of your home might be as high as 0.75 pCi/L.
- Lung cancer threat increases 16% per 2.7 pCi/L increase in radon direct exposure.
- Radon gas is a naturally-occurring by-product of the radioactive degeneration of Uranium in the dirt.
- Relying on your geographic place, the radon degrees of the air you breathe outside of your house may be as high as 0.75 pCi/L.
- The United States EPA has placed it clearly, stating, "Any kind of radon direct exposure has some threat of causing lung cancer.
If the examination results suggest radon levels at or over 4 pCi/L (picocuries per litre), the EPA advises doing a 2nd examination to verify the initial findings. If the standard of both short-term radon examinations is 4 pCi/L or greater, home owners can take actions to reduce the radon concentration. The EPA keeps in mind that given that there is no risk-free degree of radon gas direct exposure, lowering radon to below 2 pCi/L also helps reduce the number of radon-related lung cancers. Take a breath enough radon for many years, as well as it can raise your risk of lung cancer cells.
What are the symptoms of radon in your home?
If a person has been exposed to radon, 75 percent of the radon progeny in lungs will become "harmless" lead particles after 44 years. When an alpha particle damages a cell to make it cancerous, the onset of lung cancer takes a minimum of 5 years but most often 15 to 25 years, and even longer.
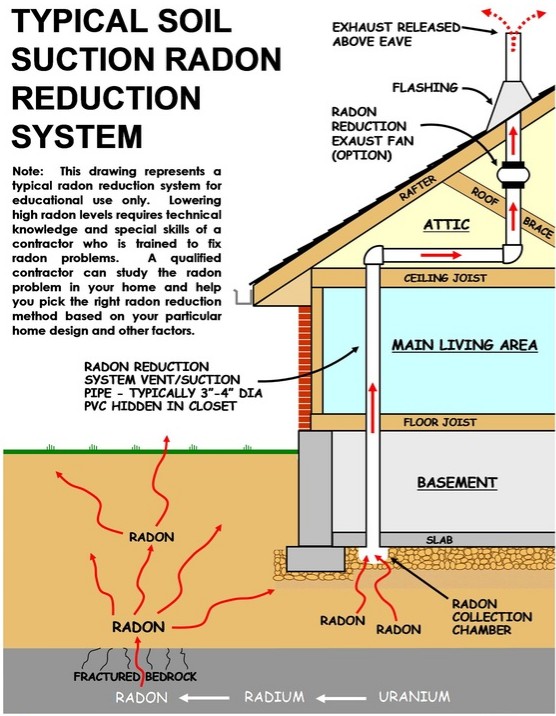

Nevertheless, when radon obtains entraped inside-- after getting in a home through joints in walls, cellar floorings, foundations as well as various other openings-- it may concentrate at hazardous levels. As a matter of fact, radon is the 2nd leading root cause of lung cancer, in charge of an estimated 21,000 fatalities every year in the United States, contributing to lung cancer's standing as the # 1 cancer cells killer. When breathed in into the lungs, it can damage DNA and also cause lung cancer cells. The EPA's recommended degree for radon mitigation is 4.0 pCi/L or above. It is however an honorable gas without any chemical affinity yet is easily affected by air activities as well as pressure.
How long does it take for radon to cause cancer?
Fact: You will reduce your risk of lung cancer when you reduce radon levels, even if you've lived with an elevated radon level for a long time. Keep in mind that radon levels below 4 pCi/L still pose some risk and that radon levels can be reduced to 2 pCi/L or below in most homes.